Ayazi syndrome
Medical condition
| Ayazi syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Choroideremia-deafness-obesity syndrome |
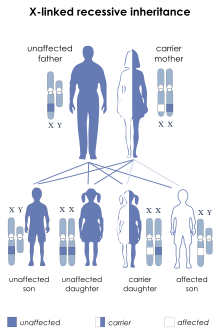 | |
| This condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive manner. | |
Ayazi syndrome (or Chromosome 21 Xq21 deletion syndrome)[1] is a syndrome characterized by choroideremia, congenital deafness and obesity.
Signs and symptoms
The presentation for this condition is as follows:[citation needed]
- Mental retardation
- Deafness at birth
- Obesity
- Choroideremia
- Impaired vision
- Progressive degeneration of the choroid
Genetics
Ayazi syndrome's inheritance pattern is described as x-linked recessive. Genes known to be deleted are CHM and POU3F4, both located on the Xq21 locus.[1]
Diagnosis
Treatment
References
- ^ a b "OMIM Entry - # 303110 - CHOROIDEREMIA, DEAFNESS, AND MENTAL RETARDATION". www.omim.org. Retrieved 2015-09-28.
- Ayazi S (1981). "Choroideremia, obesity, and congenital deafness". Am J Ophthalmol. 92 (1): 63–69. doi:10.1016/s0002-9394(14)75909-4. PMID 7258279.
- Merry DE, Lesko JG, Sosnoski DM, Lewis RA, Lubinsky M, Trask B, van den Engh G, Collins FS, Nussbaum RL (1989). "Choroideremia and deafness with stapes fixation: a contiguous gene deletion syndrome in Xq21". Am J Hum Genet. 45 (4): 530–540. PMC 1683514. PMID 2491012.
External links
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM): 303110
- v
- t
- e












