Mammalian protein found in Homo sapiens
| GGPS1 |
|---|
 |
| Available structures |
|---|
| PDB | Ortholog search: PDBe RCSB |
|---|
|
|
| Identifiers |
|---|
| Aliases | GGPS1, GGPPS, GGPPS1, geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1, MDHLO, MUDHLOV |
|---|
| External IDs | OMIM: 606982 MGI: 1341724 HomoloGene: 31267 GeneCards: GGPS1 |
|---|
| EC number | 2.5.1.1 |
|---|
| Gene location (Human) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 1 (human)[1] |
|---|
| | Band | 1q42.3 | Start | 235,327,350 bp[1] |
|---|
| End | 235,344,532 bp[1] |
|---|
|
| Gene location (Mouse) |
|---|
 | | Chr. | Chromosome 13 (mouse)[2] |
|---|
| | Band | 13 A1|13 5.29 cM | Start | 14,225,244 bp[2] |
|---|
| End | 14,238,073 bp[2] |
|---|
|
| RNA expression pattern |
|---|
| Bgee | | Human | Mouse (ortholog) |
|---|
| Top expressed in | - sperm
- ganglionic eminence
- islet of Langerhans
- optic nerve
- triceps brachii muscle
- Achilles tendon
- parotid gland
- right ventricle
- palpebral conjunctiva
- corpus epididymis
|
| | Top expressed in | - pineal gland
- medial ganglionic eminence
- lateral geniculate nucleus
- seminal vesicula
- medial vestibular nucleus
- mammillary body
- internal carotid artery
- cerebellar cortex
- ventral tegmental area
- yolk sac
|
| | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
| BioGPS | 
 | | More reference expression data |
|
|---|
|
| Gene ontology |
|---|
| Molecular function | - transferase activity
- farnesyltranstransferase activity
- protein binding
- metal ion binding
- dimethylallyltranstransferase activity
- geranyltranstransferase activity
- identical protein binding
| | Cellular component | | | Biological process | - cholesterol biosynthetic process
- farnesyl diphosphate biosynthetic process
- geranyl diphosphate biosynthetic process
- geranylgeranyl diphosphate biosynthetic process
- isoprenoid biosynthetic process
- isoprenoid metabolic process
- regulation of cholesterol biosynthetic process
| | Sources:Amigo / QuickGO |
|
| Orthologs |
|---|
| Species | Human | Mouse |
|---|
| Entrez | | |
|---|
| Ensembl | | |
|---|
| UniProt | | |
|---|
| RefSeq (mRNA) | |
|---|
NM_001037277
NM_001037278
NM_004837
NM_001371477
NM_001371478 |
| NM_010282
NM_001331119
NM_001331176
NM_001331177
NM_001331178
|
|---|
NM_001331180 |
|
|---|
| RefSeq (protein) | NP_001032354
NP_001032355
NP_001358406
NP_001358407
NP_004828
|
|---|
NP_001032354.1 |
| NP_001318048
NP_001318105
NP_001318106
NP_001318107
NP_001318109
|
|---|
NP_034412 |
|
|---|
| Location (UCSC) | Chr 1: 235.33 – 235.34 Mb | Chr 13: 14.23 – 14.24 Mb |
|---|
| PubMed search | [3] | [4] |
|---|
|
| Wikidata |
| View/Edit Human | View/Edit Mouse |
|
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GGPS1 gene.[5][6][7]
Function
This gene is a member of the prenyltransferase family and encodes a protein with geranylgeranyl diphosphate (GGPP) synthase activity. The enzyme catalyzes the synthesis of GGPP from farnesyl diphosphate and isopentenyl diphosphate. GGPP is an important molecule responsible for the C20-prenylation of proteins and for the regulation of a nuclear hormone receptor. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized.[7]
Much like its homolog farnesyl diphosphate synthase, GGPS1 is inhibited by bisphosphonate compounds.[8]
Clinical
Mutations in both copies of this gene have been associated with a syndrome of muscular dystrophy, hearing loss and ovarian insufficiency.[9]
References
- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000152904 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000021302 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Ericsson J, Greene JM, Carter KC, Shell BK, Duan DR, Florence C, Edwards PA (September 1998). "Human geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase: isolation of the cDNA, chromosomal mapping and tissue expression". Journal of Lipid Research. 39 (9): 1731–9. doi:10.1016/S0022-2275(20)32159-3. PMID 9741684.
- ^ Kainou T, Kawamura K, Tanaka K, Matsuda H, Kawamukai M (March 1999). "Identification of the GGPS1 genes encoding geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthases from mouse and human". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids. 1437 (3): 333–40. doi:10.1016/S1388-1981(99)00028-1. PMID 10101267.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: GGPS1 geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase 1".
- ^ Wiemer AJ, Wiemer DF, Hohl RJ (December 2011). "Geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase: an emerging therapeutic target". Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 90 (6): 804–12. doi:10.1038/clpt.2011.215. PMID 22048229. S2CID 27913789.
- ^ Foley AR, Zou Y, Dunford JE, Rooney J, Chandra G, Xiong H, Straub V, Voit T, Romero N, Donkervoort S, Hu Y, Markello T, Horn A, Qebibo L, Dastgir J, Meilleur K, Finkel RS, Fan Y, Mamchaoui K, Duguez S, Nelson I, Laporte J, Santi M, Malfatti E, Maisonobe T, Touraine P, Hirano M, Hughes I, Bushby K, Oppermann U, Böhm J, Jaiswal JK, Stojkovic T, Bönnemann CG (2020) GGPS1 mutations cause muscular dystrophy/hearing loss/ovarian insufficiency syndrome. Ann Neurol
Further reading
- Ericsson J, Runquist M, Thelin A, Andersson M, Chojnacki T, Dallner G (January 1993). "Distribution of prenyltransferases in rat tissues. Evidence for a cytosolic all-trans-geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 268 (2): 832–8. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)54009-6. PMID 8419360.
- Kuzuguchi T, Morita Y, Sagami I, Sagami H, Ogura K (February 1999). "Human geranylgeranyl diphosphate synthase. cDNA cloning and expression". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 274 (9): 5888–94. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.9.5888. PMID 10026212.
- Hu RM, Han ZG, Song HD, Peng YD, Huang QH, Ren SX, Gu YJ, Huang CH, Li YB, Jiang CL, Fu G, Zhang QH, Gu BW, Dai M, Mao YF, Gao GF, Rong R, Ye M, Zhou J, Xu SH, Gu J, Shi JX, Jin WR, Zhang CK, Wu TM, Huang GY, Chen Z, Chen MD, Chen JL (August 2000). "Gene expression profiling in the human hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis and full-length cDNA cloning". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 97 (17): 9543–8. Bibcode:2000PNAS...97.9543H. doi:10.1073/pnas.160270997. PMC 16901. PMID 10931946.
- Bommel H, Xie G, Rossoll W, Wiese S, Jablonka S, Boehm T, Sendtner M (November 2002). "Missense mutation in the tubulin-specific chaperone E (Tbce) gene in the mouse mutant progressive motor neuronopathy, a model of human motoneuron disease". The Journal of Cell Biology. 159 (4): 563–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.200208001. PMC 2173089. PMID 12446740.
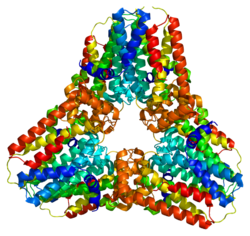
- Kavanagh KL, Dunford JE, Bunkoczi G, Russell RG, Oppermann U (August 2006). "The crystal structure of human geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase reveals a novel hexameric arrangement and inhibitory product binding". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 281 (31): 22004–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.M602603200. PMID 16698791.
- Ma J, Dempsey AA, Stamatiou D, Marshall KW, Liew CC (March 2007). "Identifying leukocyte gene expression patterns associated with plasma lipid levels in human subjects". Atherosclerosis. 191 (1): 63–72. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.05.032. PMID 16806233.
- Raz T, Nardi V, Azam M, Cortes J, Daley GQ (September 2007). "Farnesyl transferase inhibitor resistance probed by target mutagenesis". Blood. 110 (6): 2102–9. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-12-064907. PMC 1976354. PMID 17536018.
 | This article on a gene on human chromosome 1 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |



















