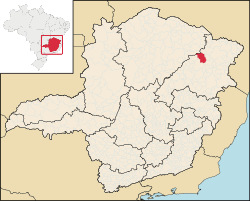
Itinga | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Country | Brazil |
| State | Minas Gerais |
| Incorporated | 31 December 1943 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | João Bosco Versiani Gusmão Cordeiro (PP) |
| Area | |
• Total | 1 649 km2 (636 sq mi) |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 15 022[1] |
| • Density | 9.1/km2 (24/sq mi) |
| Demonym | Itinguense |
| Time zone | UTC−3 (BRT) |
| Postal Code | 39610-000 |
| Area code(s) | +55 33 |
| Website | Itinga, Minas Gerais |
Itinga is a Brazilian municipality located in the northeast of the state of Minas Gerais in the Jequitinhonha River valley. As of 2020[update] the population was 15,022 in a total area of 1,641 km2.[1] The city belongs to the mesoregion of Jequitinhonha and to the microregion of Araçuaí. The elevation of the municipal seat is 269 meters. It became a municipality in 1943. Between the municipalities of Araçuaí and Itinga is located the largest lithium mine in Brazil,[2][3] explored and extracted by Sigma Lithium Resources.[4]
Etymology
[edit]The name "Itinga" is a term of Tupi origin that means "white water", through the combination of the terms 'y ("water") and ting ("white").[5]
History
[edit]The lands where the municipality of Itinga is located today were inhabited by the Botocudo tribes. Rock inscriptions by these groups are found in caves in the municipality.[6]
Non-indigenous settlement in the area began in 1810, when alferes Julião Fernandes Leão set up barracks along the Jequitinhonha River. Later, landowners built a chapel dedicated to Saint Anthony of Padua, which gave rise to the city. Settlement in the area was encouraged due to its location on the banks of the Jequitinhonha River, as it was a meeting point for tropeiros and canoeists, and because it was home to a textile factory that operated between 1880 and 1928.[6]
Itinga was part of Araçuaí until 1943, when it became a municipality.[6]
Geography
[edit]According to the regional division in force since 2017, established by the IBGE, the municipality belongs to the Intermediate Geographic Region of Teófilo Otoni and Immediate Geographic Region of Araçuaí.[7] Until then, with the divisions into microregions and mesoregions in force, it was part of the microregion of Araçuaí, which in turn was included in the mesoregion of Jequitinhonha.[8]
The city is crossed by the Jequitinhonha River and is accessed via the BR-367 highway.
Economy
[edit]The city's GDP is around R$148.3 million reais, with 47.9% of the added value coming from public administration, followed by services (28.7%), industry (13.3%) and agriculture (10.2%). The GDP per capita of Itinga is R$9.8 thousand.[9]
Culture
[edit]Itinga is renowned for its clay crafts, especially in the village of Pasmadinho, which is a town made up of artisans who produce and sell clay pots and utensils.[10] Ulisses Mendes, one of the main artisans of the Jequitinhonha Valley, lives in the town.[11]
The city's anniversary on December 31 is the biggest New Year's Eve celebration in the region, with nationally famous artists performing.[12] The city also celebrates Carnival[13] and, in September, the Nossa Senhora da Ajuda festival transforms the streets into open-air markets during the day, along with musical performances at night.[14]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b IBGE 2020
- ^ "Lítio pode impulsionar o desenvolvimento do Vale do Jequitinhonha - Assembleia Legislativa de Minas Gerais". Portal da Assembleia Legislativa de Minas Gerais (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-08-16.
- ^ "A corrida pela riqueza do lítio na pequena Araçuaí - revista piauí". revista piauí - _pra quem tem um clique a mais. 2024-07-19. Retrieved 2024-08-16.
- ^ "Sigma Lithium Resources". Sigma Lithium (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-08-16.
- ^ https://www.fflch.usp.br/dlcv/tupi/vocabulario.htm [bare URL]
- ^ a b c Tecnologia, Digitaliza. "Prefeitura Municipal de Itinga". itinga.mg.gov.br (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-08-24.
- ^ Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE) (2017). "Base de dados por municípios das Regiões Geográficas Imediatas e Intermediárias do Brasil". Retrieved 30 October 2017.
- ^ Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE) (2016). "Divisão Territorial Brasileira 2016". Retrieved 30 October 2017.
- ^ "Economia de Itinga - MG". Caravela (in Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-08-24.
- ^ Tolentino, Eustáquio (28 December 2018). "Eustáquio Tolentino Espinosa: 2115 - A arte e o amor transformam Pasmadinho". Eustáquio Tolentino Espinosa. Retrieved 2024-08-24.
- ^ Brasil, Arte Popular Do. "Arte Popular do Brasil: Ulisses Mendes". Arte Popular do Brasil. Retrieved 2024-08-24.
- ^ Gerais, Portal Minas. "Portal Minas Gerais - ANIVERSARIO DA CIDADE DE ITINGA". Portal Minas Gerais (in Brazilian Portuguese). Retrieved 2024-08-24.
- ^ "Itinga Vale Do Jequitinhonha - CarnaItinga 2023! 🎉 #CarnaItinga2023 #itingavaledojequi | Facebook". www.facebook.com. Retrieved 2024-08-24.
- ^ "Instagram". www.instagram.com. Retrieved 2024-08-24.
- Statistics from IBGE
- Indicadores Minas—info on health