Ordre des Arts et des Lettres
- View a machine-translated version of the French article.
- Machine translation, like DeepL or Google Translate, is a useful starting point for translations, but translators must revise errors as necessary and confirm that the translation is accurate, rather than simply copy-pasting machine-translated text into the English Wikipedia.
- Consider adding a topic to this template: there are already 6,158 articles in the main category, and specifying
|topic=will aid in categorization. - Do not translate text that appears unreliable or low-quality. If possible, verify the text with references provided in the foreign-language article.
- You must provide copyright attribution in the edit summary accompanying your translation by providing an interlanguage link to the source of your translation. A model attribution edit summary is
Content in this edit is translated from the existing French Wikipedia article at [[:fr:Ordre des Arts et des Lettres]]; see its history for attribution. - You should also add the template
{{Translated|fr|Ordre des Arts et des Lettres}}to the talk page. - For more guidance, see Wikipedia:Translation.
| Ordre des Arts et des Lettres | |
|---|---|
  Insignia of an Officier and a Chevalier | |
| Type | Order of merit with 3 degrees: Commandeur (Commander) Officier (Officer) Chevalier (Knight) |
| Awarded for | Significant contribution to the enrichment of the French cultural inheritance |
| Presented by | French Minister of Culture |
| Status | Active |
| Established | 2 May 1957 |
| Website | http://www.culture.gouv.fr/culture/artsetlettres/ |
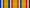
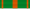
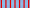
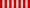
 Commandeur  Officier  Chevalier Ribbon bars of the Order | |
| Precedence | |
| Next (higher) | Ordre du Mérite Maritime |
| Next (lower) | Médaille des Évadés |
The Ordre des Arts et des Lettres (French for 'Order of Arts and Letters') is an order of France established on 2 May 1957 by the Minister of Culture. Its supplementary status to the Ordre national du Mérite was confirmed by President Charles de Gaulle in 1963. Its purpose is the recognition of significant contributions to the arts, literature, or the propagation of these fields.
Its origin is attributed to the Order of Saint Michael (established 1 August 1469), as acknowledged by French government sources.[1][2][3]
Background
To be considered for the award, French government guidelines stipulate that citizens of France must be at least thirty years old, respect French civil law, and must have "significantly contributed to the enrichment of the French cultural inheritance".
Membership is not, however, limited to French nationals; recipients include numerous foreign luminaries. Foreign recipients are admitted into the Order "without condition of age".
The Order has three grades:
- Commandeur (Commander) — medallion worn on a necklet; up to 20 recipients a year
- Officier (Officer) — medallion worn on a ribbon with rosette on left breast; up to 60 recipients a year
- Chevalier (Knight) — medallion worn on a ribbon on left breast; up to 200 recipients a year
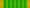
The médaille (medallion) of the Order is an eight-pointed, green-enameled asterisk, in gilt for Commanders and Officers and in silver for Knights; the obverse central disc has the letters "A" and "L" on a white-enameled background, surrounded by a golden ring emblazoned with the phrase République Française. The reverse central disc features the head of Marianne on a golden background, surrounded by a golden ring bearing the words Ordre des Arts et des Lettres. The Commander's badge is topped by a gilt twisted ring.
The ribbon of the Order is green with four white stripes.
Members of the Order

According to the statutes of the Order, French citizens must wait a minimum of 5 years before they are eligible to be upgraded from Chevalier to Officier, or Officier to Commandeur, and must have displayed additional meritorious deeds than just those that originally made them a Chevalier. However, in the statutes, there is a clause saying "Les Officiers et les Commandeurs de la Légion d'honneur peuvent être directement promus à un grade équivalent dans l'Ordre des Arts et des Lettres". (Translation: "The officers and commanders of the Legion of Honour can be promoted directly to an equivalent grade in the Order of Arts and Letters".) This means that if someone were to be made Officier of the Legion of Honour, then the next year, that person could be directly made Officier of the Order of Arts and Letters and bypass a nomination as a knight and the five-year rule.
See also
- Ribbons of the French military and civil awards
- Ordre des arts et des lettres du Québec, a Quebec order based in part on the Ordre des Arts et des Lettres
References
External links

- "Nominations dans l'Ordre des Arts et Lettres" (in French). Ministry of Culture (France). 2007. Archived from the original on 10 February 2009. Retrieved 6 February 2009.
- v
- t
- e
| National | |
|---|---|
| Ministerial |
|
| Territorial |
| 1852 – 1871: Second Empire | |
|---|---|
| 1871–1914: Belle Époque | |
| 1914–1918: World War I |
|
| 1918–1939: Interwar | |
| 1939–1945: World War II |
|
| 1945–1964: Decolonisation |
|
| Since 1964 |
| Royal & Imperial |
|
|---|---|
| Ministerial |
|
| Colonial |
|
 France portal
France portal