内頸静脈


内頸静脈(ないけいじょうみゃく、internal jugular vein)は、脳、顔面表層および頸部の血液を集める静脈で左右合計二本ある。
経路
二本の静脈はS状静脈洞に直接連続しており、頭蓋骨の付け根にある頸静脈孔の後部より始まる。開始地点では少し膨張しており、これを内頸静脈上球と呼ぶ。下顎後静脈前枝、顔面静脈、舌静脈に共通幹を持つ。
頸部の側面において、内頸動脈の後方で下に降りて行き、その後総頸動脈の前外側を走る。首の付け根の部分で、鎖骨下静脈と合流して腕頭静脈となる。末端の少し上に二つ目の膨張があり、これを内頸静脈下球と呼ぶ。
外側頭直筋の上を通り、内頸動脈と頸静脈孔を通る神経の後方を通る。下部において、内頸動静脈は同じ面を通り、舌咽神経と舌下神経が動静脈の間を通る。迷走神経は頸動脈鞘において動静脈の間を通る。副神経は内頸静脈の前方であることも後方であることもあるが、斜め後方に向けて走行する。
首の付け根において、右側内頸静脈は総頸動脈に近く、鎖骨下動脈の基部と交差する。左側内頸静脈は総頸動脈と重なる。
通常、左側内頸静脈は右側より短く、それぞれが静脈の一番後ろからおよそ2.5cmの場所に1組の弁を持っている。
合流する静脈
内頸静脈に合流する静脈としては以下のものがある。[1]
臨床的関連
内頸静脈は比較的浅側にあり、骨や軟骨といった組織に保護されていない。これによりダメージを受けやすい。大量の血液が流れるため、内頸静脈の損傷はすぐに出血性ショックを引き起こし、適切な処置が行わなければ死亡する。
頸静脈圧
右心房と内頸静脈の間に全く弁がない場合、右心房の中の圧力が十分高まったとき、血液が内頸静脈に逆流する。これは外部から観察でき、心房の圧力を評価することができる。この脈動を頸静脈圧(JVP)とよぶ。通常、患者が頭を観察者から45度回転させることによって確認される。いくつかの症状で上昇が認められる。[2]
また、肝臓に圧力をかけることで人工的にJVPを上昇させることができる。(肝頸静脈逆流)これはJVPの場所を見つけ、頸動脈波との区別を行うのに使用される。頸動脈波と異なり、頸静脈圧は微細である。
カテーテル
内頸静脈は大きく、体の中央にあり、比較的浅側にあるため、しばしば中心静脈カテーテル(CV)の挿入場所として用いられる。CVはいくつかの理由で挿入される。たとえば正確に中心静脈圧の測定が必要な場合や薬などを入れる必要がある場合、末梢静脈の場所を見つけにくい蘇生中の患者などがある。
内頸静脈の位置は、ほとんど異ならないので、他の静脈に比べ、場所を見つけやすい。しかしながら、時々挿入に失敗し、他の組織たとえば頸動脈や迷走神経を傷つけてしまうことがある。
画像
-
 Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra.
Section of the neck at about the level of the sixth cervical vertebra. -
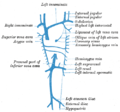 Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins.
Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins. -
 Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries.
Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries. -
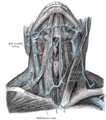 The veins of the neck, viewed from in front.
The veins of the neck, viewed from in front. -
 The vertebral vein.
The vertebral vein. -
 The venæ cavæ and azygos veins, with their tributaries.
The venæ cavæ and azygos veins, with their tributaries. -
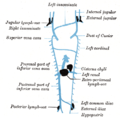 Scheme showing relative positions of primary lymph sacs.
Scheme showing relative positions of primary lymph sacs. -
 The thoracic and right lymphatic ducts.
The thoracic and right lymphatic ducts. -
 Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and sphenopalatine ganglion.
Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and sphenopalatine ganglion. -
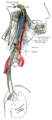 Course and distribution of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves.
Course and distribution of the glossopharyngeal, vagus, and accessory nerves. -
 Hypoglossal nerve, cervical plexus, and their branches.
Hypoglossal nerve, cervical plexus, and their branches. -
 Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves.
Muscles of the pharynx, viewed from behind, together with the associated vessels and nerves. -
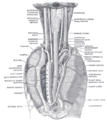 The position and relation of the esophagus in the cervical region and in the posterior mediastinum. Seen from behind.
The position and relation of the esophagus in the cervical region and in the posterior mediastinum. Seen from behind. -
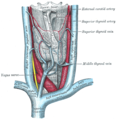 The thyroid gland and its relations.
The thyroid gland and its relations. -
 The thymus of a full-term fetus, exposed in situ.
The thymus of a full-term fetus, exposed in situ.





















