Insulinski receptor
| insulin receptor | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifikatori | |||||||||||||||
| Alijasi | |||||||||||||||
| Spoljašnji ID | GeneCards: [1] | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Ortolozi | |||||||||||||||
| Vrste | Čovek | Miš | |||||||||||||
| Entrez |
|
| |||||||||||||
| Ensembl |
|
| |||||||||||||
| UniProt |
|
| |||||||||||||
| RefSeq (mRNA) |
|
| |||||||||||||
| RefSeq (protein) |
|
| |||||||||||||
| Location (UCSC) | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||
| PubMed search | n/a | n/a | |||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Insulinski receptor (IR) je transmembranski receptor koji aktiviraju insulin, IGF-I, IGF-II, i koji pripada velikoj klasi receptorskih tirozinskih kinaza.[1] U pogledu metabolizma, insulinskih receptor ima ključnu ulogu u regulaciji glukozne homeostaze, funkcionalnog procesa koji pod degenerivnim okolnostima može da dovede do niza kliničkih manifestacija, uključujući dijabetes i kancer.[2][3] Biohemijski, insulinski receptor je kodiran jednim genom INSR, iz koga se alternativnim splajsovanjem tokom transkripcije formiraju bilo IR-A ili IR-B izoforma.[4] Dalje posttranslacione izmene ovih izoformi dovode do formiranja proteolitički skraćenih α i β podjedinica, koje nakon kombinovanja imaju sposobnost formiranja homo ili hetero-dimera, čime nastaje ≈320 kDa disulfidno vezani transmembranski insulinski receptor.[4]
Interakcija
Insulinski receptor formira interakcije sa
Referencs
- ^ Ward CW, Lawrence MC (2009). „Ligand-induced activation of the insulin receptor: a multi-step process involving structural changes in both the ligand and the receptor”. BioEssays. 31 (4): 422—34. PMID 19274663. doi:10.1002/bies.200800210.
- ^ Ebina Y, Ellis L (1985). „The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling.”. Cell. 40 (4): 747—58. PMID 2859121. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4.
- ^ Malaguarnera R, Belfiore A (2012). „Proinsulin Binds with High Affinity the Insulin Receptor Isoform A and Predominantly Activates the Mitogenic Pathway.”. Endocrinology. Epub (5): 2152—63. PMID 22355074. doi:10.1210/en.2011-1843.
- ^ а б Belfiore A, Frasca F (2009). „Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease.”. Endocr Rev. 30 (6): 586—623. PMID 19752219. doi:10.1210/er.2008-0047.
- ^ Maddux BA, Goldfine ID (2000). „Membrane glycoprotein PC-1 inhibition of insulin receptor function occurs via direct interaction with the receptor alpha-subunit”. Diabetes. 49 (1): 13—9. PMID 10615944. doi:10.2337/diabetes.49.1.13.
- ^ Langlais P, Dong LQ, Hu D, Liu F (2000). „Identification of Grb10 as a direct substrate for members of the Src tyrosine kinase family”. Oncogene. 19 (25): 2895—903. PMID 10871840. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203616.
- ^ Hansen H, Svensson U, Zhu J, Laviola L, Giorgino F, Wolf G, Smith RJ, Riedel H (1996). „Interaction between the Grb10 SH2 domain and the insulin receptor carboxyl terminus”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (15): 8882—6. PMID 8621530. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.15.8882.
- ^ Liu F, Roth RA (1995). „Grb-IR: a SH2-domain-containing protein that binds to the insulin receptor and inhibits its function”. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 92 (22): 10287—91. Bibcode:1995PNAS...9210287L. PMC 40781
 . PMID 7479769. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10287.
. PMID 7479769. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.22.10287. - ^ He W, Rose DW, Olefsky JM, Gustafson TA (1998). „Grb10 interacts differentially with the insulin receptor, insulin-like growth factor I receptor, and epidermal growth factor receptor via the Grb10 Src homology 2 (SH2) domain and a second novel domain located between the pleckstrin homology and SH2 domains”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (12): 6860—7. PMID 9506989. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.12.6860.
- ^ Frantz JD, Giorgetti-Peraldi S, Ottinger EA, Shoelson SE (1997). „Human GRB-IRbeta/GRB10. Splice variants of an insulin and growth factor receptor-binding protein with PH and SH2 domains”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (5): 2659—67. PMID 9006901. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.5.2659.
- ^ Kasus-Jacobi A, Béréziat V, Perdereau D, Girard J, Burnol AF (2000). „Evidence for an interaction between the insulin receptor and Grb7. A role for two of its binding domains, PIR and SH2”. Oncogene. 19 (16): 2052—9. PMID 10803466. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1203469.
- ^ Aguirre V, Werner ED, Giraud J, Lee YH, Shoelson SE, White MF (2002). „Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (2): 1531—7. PMID 11606564. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101521200.
- ^ Sawka-Verhelle D, Tartare-Deckert S, White MF, Van Obberghen E (1996). „Insulin receptor substrate-2 binds to the insulin receptor through its phosphotyrosine-binding domain and through a newly identified domain comprising amino acids 591-786”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 271 (11): 5980—3. PMID 8626379. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.11.5980.
- ^ O'Neill TJ, Zhu Y, Gustafson TA (1997). „Interaction of MAD2 with the carboxyl terminus of the insulin receptor but not with the IGFIR. Evidence for release from the insulin receptor after activation”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 272 (15): 10035—40. PMID 9092546. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.15.10035.
- ^ Braiman L, Alt A, Kuroki T, Ohba M, Bak A, Tennenbaum T, Sampson SR (2001). „Insulin induces specific interaction between insulin receptor and protein kinase C delta in primary cultured skeletal muscle”. Molecular Endocrinology. 15 (4): 565—74. PMID 11266508. doi:10.1210/mend.15.4.0612.
- ^ Rosenzweig T, Braiman L, Bak A, Alt A, Kuroki T, Sampson SR (2002). „Differential effects of tumor necrosis factor-alpha on protein kinase C isoforms alpha and delta mediate inhibition of insulin receptor signaling”. Diabetes. 51 (6): 1921—30. PMID 12031982. doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.6.1921.
- ^ Maegawa H, Ugi S, Adachi M, Hinoda Y, Kikkawa R, Yachi A, Shigeta Y, Kashiwagi A (1994). „Insulin receptor kinase phosphorylates protein tyrosine phosphatase containing Src homology 2 regions and modulates its PTPase activity in vitro”. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 199 (2): 780—5. PMID 8135823. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1994.1297.
- ^ Kharitonenkov A, Schnekenburger J, Chen Z, Knyazev P, Ali S, Zwick E, White M, Ullrich A (1995). „Adapter function of protein-tyrosine phosphatase 1D in insulin receptor/insulin receptor substrate-1 interaction”. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 270 (49): 29189—93. PMID 7493946. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.49.29189.
- ^ Kotani K, Wilden P, Pillay TS (1998). „SH2-Balpha is an insulin-receptor adapter protein and substrate that interacts with the activation loop of the insulin-receptor kinase”. The Biochemical Journal. 335 ( Pt 1) (1): 103—9. PMC 1219757
 . PMID 9742218. doi:10.1042/bj3350103.
. PMID 9742218. doi:10.1042/bj3350103. - ^ Nelms K, O'Neill TJ, Li S, Hubbard SR, Gustafson TA, Paul WE (1999). „Alternative splicing, gene localization, and binding of SH2-B to the insulin receptor kinase domain”. Mammalian Genome. 10 (12): 1160—7. PMID 10594240. doi:10.1007/s003359901183.
Literatura
- Pearson RB, Kemp BE (1991). „Protein kinase phosphorylation site sequences and consensus specificity motifs: tabulations”. Methods in Enzymology. 200: 62—81. PMID 1956339. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(91)00127-I.
- Joost HG (1995). „Structural and functional heterogeneity of insulin receptors”. Cellular Signalling. 7 (2): 85—91. PMID 7794689. doi:10.1016/0898-6568(94)00071-I.
- O'Dell SD, Day IN (1998). „Insulin-like growth factor II (IGF-II)”. The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 30 (7): 767—71. PMID 9722981. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(98)00048-X.
- Lopaczynski W (1999). „Differential regulation of signaling pathways for insulin and insulin-like growth factor I”. Acta Biochimica Polonica. 46 (1): 51—60. PMID 10453981.
- Sasaoka T, Kobayashi M (2000). „The functional significance of Shc in insulin signaling as a substrate of the insulin receptor”. Endocrine Journal. 47 (4): 373—81. PMID 11075717. doi:10.1507/endocrj.47.373.
- Perz M, Torlińska T (2001). „Insulin receptor--structural and functional characteristics”. Medical Science Monitor. 7 (1): 169—77. PMID 11208515.
- Benaim G, Villalobo A (2002). „Phosphorylation of calmodulin. Functional implications”. European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 269 (15): 3619—31. PMID 12153558. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03038.x.
Spoljašnje veze
- Insulin+receptor на US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- п
- р
- у
-
 1gag: Kristalna struktura insulinske receptorske kinaze u kompleksu sa bisupstratnim inhibitorom
1gag: Kristalna struktura insulinske receptorske kinaze u kompleksu sa bisupstratnim inhibitorom -
 1i44: Kristalografske studije aktivacije mutanta petlje insulinske receptorske tirozinske kinaze
1i44: Kristalografske studije aktivacije mutanta petlje insulinske receptorske tirozinske kinaze -
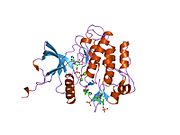 1ir3: Fosforilisana insulinska receptorska tirozinska kinaza u kompleksu sa peptidnim supstratom i ATP analogom
1ir3: Fosforilisana insulinska receptorska tirozinska kinaza u kompleksu sa peptidnim supstratom i ATP analogom -
 1irk: Kristalna struktura tirozinskog kinaznog domena ljudskog insulinskog receptora
1irk: Kristalna struktura tirozinskog kinaznog domena ljudskog insulinskog receptora -
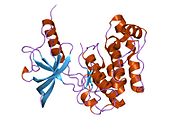 1p14: Kristalna struktura katalitičke petlje mutanta insulinske receptorske tirozinske kinaze
1p14: Kristalna struktura katalitičke petlje mutanta insulinske receptorske tirozinske kinaze -
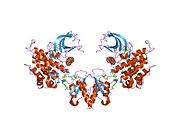 1rqq: Kristalna struktura insulinske receptorske kinaze u kompleksu sa SH2 domenom APS
1rqq: Kristalna struktura insulinske receptorske kinaze u kompleksu sa SH2 domenom APS -
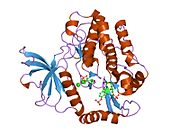 2auh: Kristalna struktura Grb14 BPS regiona kompleksa sa insulinskom receptorskom tirozinskom kinazom
2auh: Kristalna struktura Grb14 BPS regiona kompleksa sa insulinskom receptorskom tirozinskom kinazom -
 2b4s: Kristalna struktura kompleksa PTP1B i insulinske receptorske tirozinske kinaze
2b4s: Kristalna struktura kompleksa PTP1B i insulinske receptorske tirozinske kinaze -
 2dtg: Insulinski receptor (IR) ektodomain u kompleksu sa fabovima
2dtg: Insulinski receptor (IR) ektodomain u kompleksu sa fabovima -
 2hr7: Insulinski receptor (domeni 1-3)
2hr7: Insulinski receptor (domeni 1-3)






















