| Jaipur Metro | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 | |||
 Jaipur Metro Pink line at Chandpole station | |||
| Overview | |||
| Owner | Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation Limited (JMRC) | ||
| Locale | Jaipur, Rajasthan, India | ||
| Transit type | Rapid Transit | ||
| Number of lines | 1(operational) 1(planned) | ||
| Line number | Operational: Planned: | ||
| Number of stations | 11[1] | ||
| Daily ridership | 55,068 (July 2024)[2] | ||
| Chief executive | Nihal Chand Goel, Chairman & MD[3] | ||
| Headquarters | Khanij Bhavan, C-Scheme, Jaipur | ||
| Website | Jaipur Metro | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 3 June 2015[1] | ||
| Operator(s) | Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation (JMRC) | ||
| Train length | 4 coaches | ||
| Headway | 10 minutes (peak) 15 minutes (off-peak)[4] | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 11.97 km (7.44 mi)[1] | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | 25 kV 50 Hz AC overhead catenary | ||
| Average speed | 32 km/h (20 mph) | ||
| Top speed | 80 km/h (50 mph)[5] | ||
| |||
The Jaipur Metro is a rapid transit system in the city of Jaipur, Rajasthan, India.[6] Construction on the mostly elevated part of the first line, called Phase 1A, comprising 9.63 kilometres (5.984 mi) of route from Mansarovar to Chandpole Bazaar,[1] started in November 2010,[7] and was completed in 2014. The Jaipur Metro began commercial service between Chandpole and Mansarovar on 3 June 2015.[5] The Jaipur Metro is the first metro in India to run on triple-storey elevated road and metro track. Phase 1-B, from Chandpole to Badi Chaupar, began operation on 23 September 2020.[8][9]
History
[edit]JMRC Ltd.
[edit]The Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation Ltd., abbreviated to JMRC, is a state-owned company[10] that operates the Jaipur Metro. The Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation Ltd. was created on 1 January 2010.[11] Among the Rapid Transit systems of India, it has been recorded fastest to conduct of trial run after starting construction, when it commenced trial runs in Jaipur on 18 September 2013 flagged off by the then Chief Minister of Rajasthan Shri Ashok Gehlot.
Construction
[edit]Physical construction work on the Jaipur Metro started on 24 February 2011.[1] JMRC consulted the DMRC on rapid transit operation and construction techniques.
The first line of the Jaipur Metro was opened to public by Vasundhara Raje, the Chief Minister of Rajasthan, on 3 June 2015,[12] and thus, it became the sixth rapid transit system in India. Phase 1-B of the project started operating on 23 September 2020.[8][9]
Network
[edit]
The Jaipur Metro is being built in 2 phases. Phase 1 consists of the Pink Line[1] and Phase 2 consists of the Orange Line. Currently[when?], the Orange Line is being planned. The implementation of Phase 1A of the project (Mansarover to Chandpole having the length of about 9.63 km (5.984 mi)) including the civil works, permanent way, depot and traction and power supply, etc. was being managed by DMRC.[13][14] Phase I-A completed 9 stations and 9.63 kilometres (5.984 mi) of route length,[1] of which 0.95 kilometres (0.590 mi) is underground and 9.13 kilometres (5.673 mi) is elevated.
The remainder of the first line, Phase 1-B [2.34 kilometres (1.454 mi), 2 stations], got completed by 23 September 2020.[15] Phase 2 (23.099 kilometres (14.353 mi), 20 stations)[15] is planned to be completed by 2021.[citation needed] With the completion of Phases 1 and 2, the network will span a 35.078 kilometres (21.796 mi) and 31 stations.[15]
Pink Line
[edit]
The first route of Jaipur Metro (East-West Corridor) connect Mansarovar to Badi Chaupar via Civil Lines and Chandpole. In Phase I-A, the metro was operating between Mansarovar to Chandpole. The construction of Phase-1B between Chandpole and Badi Chaupar is completed. This is the Metro line that got flagged off on 5 June 2015, and has been named as Pink Line, as it takes passengers to the Pink City.[1] The depot for this line is situated at Mansarovar.[16]
Jaipur Metro was planned to be built in phases. Phase-1A (9.63 km (5.984 mi)) was completed in 2014, and Phase-1B was completed in 2020 and Phase II is scheduled for completion in 2020.[17]
Phase 1B
[edit]The Pink Line was realized with the completion of Phase 1B (2.34 kilometres (1.454 mi), 2 stations), which got completed in September 2020.[17][8][9] The tunnel excavation work between Chandpole and Badi Chaupar completed in August 2017,[18] civil work to complete by October 2019.[19] Trial running completed in January 2020.[20] On 23 September 2020 it has been opened to public. It now completes the Pink Line. Details of the line are:
| Line | Stations | Length (km) |
Terminals | No. of interchanges planned | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pink Line extension | 2 | 2.349 | Chandpole | Badi Chaupar | 0 |
Phase 1C
[edit]For Phase 1C, Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation (JMRC) plans to extend the Pink Line from Badi Chaupar to Transport Nagar. For the same, the corporation has prepared a detailed project report (DPR) of Phase 1C by taking public suggestions. According to the DPR, the estimated project cost will be Rs 856 crore, including cost of land and taxes, The total length of the project will be 3.412 km (2.120 mi) (2.452 km (1.524 mi) Underground and 0.96 km (0.597 mi) Elevated), with 1 underground station at Ramganj Chaupar and 1 elevated station at Transport Nagar. This project was expected to be completed until March 2025 however it has missed its deadline. Once constructed, the estimated ridership between the entire stretch, Mansarovar to Transport Nagar, will be over 1.38 lakh till 2031.[21][22]
| Line | Stations | Length (km) |
Terminals | No. of interchanges planned | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pink Line extension | 2 | 3.412 | Badi Chaupar | Transport Nagar | 0 |
Phase 1D
[edit]For Phase 1D, Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation (JMRC) plans to extend the Pink Line from Mansarovar to Ajmer Road. For the same, the corporation has prepared a detailed project report (DPR) of Phase 1D by taking public suggestions. According to the DPR, The total length of the project will be 1.312 km all elevated, with 1 elevated station at Ajmer Road and a 0.357 km loop line.
| Line | Stations | Length (km) |
Terminals | No. of interchanges planned | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pink Line extension | 1 | 1.312 | Mansarovar | Ajmer Road | 0 |
Phase 2
[edit]Phase 2 (North-South Corridor) which is being planned by the authorities. The Orange Line will be 23.099 kilometres (14.353 mi) and serve 20 stations when complete.[15] This will connect Sitapura Industrial Area in the South to Ambabari in the North via Ajmeri Gate and MI Road. The tracks will be elevated between Sitapura and Ajmeri Gate and then will go underground. There might be some changes in plan before actual construction starts on these lines.
| Line | Stations | Length (km) |
Terminals | No. of interchanges planned | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Orange Line | 19 | 23.099 | Sitapura Industrial Area | Ambabari | 1 |
Current route
[edit]As of September 2020[update], with the completion and the beginning of operations of Phase 1, the Jaipur Metro network comprises 1 line, serving 11 metro stations[23] and operating on a total route length of 9.63 kilometres (5.98 mi).[1]
| Line | First operational | Last extension | Stations | Length (km) |
Termini | Rolling stock | Track gauge (mm) |
Power | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pink Line | 3 June 2015 | 23 September 2020 | 11 | 11.97 | Mansarovar | Badi Chaupar | 10 trains[24] | 1435 | 25 kV OHE |
| TOTAL | 11 | 11.97 | |||||||
Finances
[edit]Estimated cost of the east–west corridor of the Jaipur Metro is ₹3,149 crore (US$370 million).[24] The state government would be directly funding ₹600 crore (US$71 million) while the rest would be borne by other wings of state urban development and housing departments. The Phase-II is expected to cost ₹6,583 crore (US$780 million) crore for which government is mulling over PPP mode.[25]
Operations
[edit]
A concession for operation and maintenance of the Stage 1 and Stage 2 is to be let on PPP basis.[26]

Trains operate at a frequency of 10 to 15 minutes between 5:30 and 22:30 depending peak and off-peak time. Trains operating within the network typically travel at speed up to 40 km/h (25 mph), and stop for about 20–40 seconds at each station. Automated station announcements are recorded in Hindi and English. Many stations have services such as Parking lot, ATMs and mobile recharge. The metro also has a sophisticated fire alarm system for advance warning in emergencies, and fire retardant material is used in trains as well as on the premises of stations. Navigation information will sooner be available on Google Transit. The first coach of every train is reserved for women.[citation needed]
Security
[edit]The responsibility of security of Jaipur Metro has been entrusted to Rajasthan Police. A strength of 789 police personnel has been sanctioned for security and policing of Jaipur Metro. Latest security equipments have been provided at all Metro Stations.[1] Closed-circuit cameras from IndigoVision are used to monitor trains and stations, and feed from these is monitored by Rajasthan Police and Jaipur Metro authorities at their respective control rooms. In addition metal detectors, X-ray baggage inspection systems, and dog squads are also deployed which are used to secure the system. Each of the underground stations has about 45 to 50 cameras installed while the elevated stations have about 16 to 20 cameras each. The monitoring of these cameras is done by the Rajasthan Police, which is in charge of security of the Metro, as well as the Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation. Intercoms are provided in each train car for emergency communication between the passengers and the train operator. Periodic security drills are carried out at stations and on trains to ensure preparedness of security agencies in emergency situations.
Ticketing & Recharge
[edit]For the convenience of customers, Jaipur Metro commuters have three choices for ticket purchase. The RFID tokens are valid only for a single journey on the day of purchase and the value depends on the distance travelled, with fares for a single journey ranging from ₹5 (5.9¢ US) to ₹15 (18¢ US). Fares are calculated based on the origin and destination stations using a fare chart and it also depends on peak rush in Metro.[1] Travel cards are available for longer durations and are most convenient for frequent commuters. They are valid for three years from the date of purchase or the date of last recharge, and are available in denominations of ₹100 (US$1.20) to ₹1,000 (US$12). 10%-15% discount is given on travels made on it depending on actual fare.[1] A deposit of ₹50 (59¢ US) needs to be made to buy a new card which is refundable on the return of the card any time before its expiry if the card is not physically damaged. Tourist cards can be used for unlimited travel on the Jaipur Metro network over short periods of time. There are two kinds of tourist cards valid for one and three days respectively. The cost of a one-day card is ₹50 (59¢ US) and that of a three-day card is ₹150 (US$1.80), besides a refundable deposit of ₹50 (59¢ US) that must be paid at the time of purchasing the card. Jaipur Metro also has introduced a Combo Card. JMRC has already entered into a MoU with HDFC Bank and accordingly co-branded Combo Cards will be issued by HDFC Bank which will be used on Jaipur Metro system just like Daily Commuter Smart Cards issued by Jaipur Metro.
Rolling stock
[edit]The Metro uses 1,435 mm (4 ft 8+1⁄2 in) standard gauge rolling stock. Trains are maintained at Mansarovar Deport for Pink Line. In December 2011 BEML was awarded a ₹318 crore (US$38 million) contract to supply 10 four-car trains for Phase 1.[13] The Jaipur Metro plans to lengthen the trains later to 6 coaches as the traffic increases.[27] BEML expects a follow-on order worth ₹60 crore (US$7.1 million)
Thus these rolling stocks are said to be indigenous and are manufactured by BEML at its factory in Bangalore. The trains are four-car consists with a capacity of 1506 commuters per train, accommodating 50 seated and 292 standing passengers in each coach. These trains will have CCTV cameras in and outside the coaches, power supply connections inside coaches to charge mobiles and laptops, humidity control, microprocessor-controlled disc brakes, and will be capable of maintaining an average speed of 32 km/h (20 mph) over a distance of 1.1 km (0.68 mi).
Trains on the metro operate at a maximum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph), and an average speed of 32 km/h (20 mph). Maximum speed is limited to 42 km/h (26 mph) at curves.[28]
The Rolling Stock used on this line is similar to the Rolling stock on the Violet and Green Lines on Delhi Metro
Signalling and Telecommunication
[edit]The Jaipur Metro uses cab signalling along with a centralised automatic train control system consisting of Automatic Train Protection and automatic train signalling modules.[24] Jaipur Metro has proposed that it will have automatic train operation also in future. A 380 MHz digital trunked TETRA radio communication system from Cassidian is used on all lines to carry both voice and data information. An integrated system comprising optical fibre cable, on-train radio, CCTV, and a centralised clock and public address system is used for telecommunication during train operations as well as emergencies.[24]
Artwork
[edit]Jaipur Metro has been decorated by the artwork of heritage wall of Jaipur inside and outside of the Metro. Metro stations also have the same kind of artwork.
Controversies
[edit]On 10 March 2011, the Rajasthan High Court issued show cause notices to state authorities, JMRC, and JDA's land acquisition officer, on petition by some shop owners from Station Road, asking them to justify the Jaipur Metro Project, as petitioners alleged no proper survey was done before construction of the Pink Line began.[29]
There were some accidents at the Metro project site, injuring laborers and passers-by, attracting criticism for lack of security measures.[30] In one incident, an 18-foot-long (5.5 m) wall collapsed, killing two men. A case was registered against the firm DSC Limited which was involved in construction.[31] There were reports of heightened fears among people that sub-letting of the work by the major contractors could be compromising the safety standards.[32]
Phase I-B is also not in accordance with Jaipur's archaeological laws, which states that any kind of digging/tunneling work in the vicinity of heritage sites is not allowed. According to the archaeological laws, whoever destroys, injures, mutilates, defaces, alters, removes, disperses, misuses, imperils or allows to fall into decay a protected monument, or removes from a protected monument any sculpture, carving image, bas-relief, inscription or other like object, shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to six months with a fine which may extend to five thousand rupees or with both.[33][34]
The project also caused huge losses of business activities of shopkeepers, as the city's market will remain either closed or operative in barricades only.[35][36]
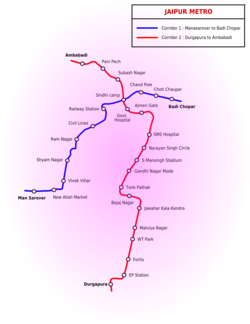
Network Map
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l "Jaipur Metro A Brief Note on the Project" (PDF). JMRC. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Passenger Travelled Count". Transport Department Of Rajasthan.
- ^ "JMRC". Jaipurmetrorail.in. 20 January 2010. Retrieved 28 September 2013.
- ^ "No more long wait as Metro set to up trips to 170 per day from Friday - Times of India". The Times of India. 21 June 2018. Retrieved 22 June 2018.
- ^ a b "Jaipur Metro gets final safety nod, may start in May end". The Times of India. 2 May 2015.
- ^ "How metro rail networks are spreading across India". 26 July 2017.
- ^ "Jaipur: Metro project to begin on Saturday". NDTV. 12 November 2010.
- ^ a b c "JMRC all set to start Metro on Phase-IB corridor by mid-November | Jaipur News - Times of India". The Times of India. 4 November 2019.
- ^ a b c "We are not going to implement CAA in the state: Dhariwal - First India News Paper". www.firstindia.co.in. Archived from the original on 11 January 2020.
- ^ "Project Introduction". Archived from the original on 6 July 2018. Retrieved 9 May 2015.
- ^ "About JMRC". JMRC. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Rajasthan CM launches Jaipur metro". The Hindu. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b "BEML wins Jaipur metro train contract". Railway Gazette International. 22 December 2011. Archived from the original on 29 February 2012. Retrieved 26 January 2012.
- ^ "Execution of Stage 1 and 2". JMRC. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Present Status of the Project". JMRC. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "New Metro MD reviews project". www.daily.bhaskar.com. Archived from the original on 5 March 2012. Retrieved 27 May 2012.
- ^ a b "Work on Jaipur Metro 1B to start next year | Jaipur News - Times of India". The Times of India. 4 June 2019.
- ^ "Tunnel excavation for Jaipur Metro between Chandpole and Badi Chaupar completed". 11 August 2017.
- ^ "Phase 1-B of Jaipur Metro to be completed by October, likely to be operational by year-end". Hindustan Times. 4 June 2019.
- ^ "Jaipur Metro completes important link". 30 January 2020.
- ^ "JMRC plans to extend Badi Chaupar corridor". The Times of India. 31 January 2021.
- ^ "Jaipur Metro Publishes Phase 1C & Phase 2 DPRs for Finalization". 1 February 2021.
- ^ "Metro Station Numbers". JMRC. Archived from the original on 18 May 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d "DPR Phase I" (PDF). JMRC. p. 3. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 April 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "DPR Phase II" (PDF). JMRC. p. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 April 2015. Retrieved 3 June 2015.
- ^ "Urban rail news in brief". Railway Gazette International. 17 July 2011. Archived from the original on 9 September 2012.
- ^ Ajay Singh (22 February 2011). "First phase Metro to have four coaches". The Times of India. Archived from the original on 8 September 2012. Retrieved 10 July 2011.
- ^ "Jaipur Metro run delayed again as safety check yet to be done". The Times of India.
- ^ "Court to state: Justify Jaipur Metro project". The Times of India. 10 March 2011. Archived from the original on 8 September 2012. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "5 injured in yet another metro worksite accident". The Times of India. 10 June 2011. Archived from the original on 8 September 2012. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Case registered in Jaipur Metro rail accident". Press Trust of India. 13 May 2011. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 11 July 2011.
- ^ "Subletting raises fears of compromising Metro work". The Times of India. 16 May 2011. Archived from the original on 8 September 2012. Retrieved 16 July 2011.
- ^ "Department of Archaeology & Museums, Rajasthan" (PDF).
- ^ http://rajasthanpatrika.patrika.com/news/archaeological-against-the-law-subway-tunnel/1173901.html#login_form Archived 7 September 2014 at the Wayback Machine [bare URL]
- ^ http://rajasthanpatrika.patrika.com/news/market-may-shut-down-three-year-in-jaipur/1177167.html#login_form Archived 7 September 2014 at the Wayback Machine [bare URL]
- ^ "परकोटे में मेट्रो के खिलाफ त्रिपोलिया के व्यापारी - Tripolians against the wall of the subway merchant - Rajasthan Patrika". Archived from the original on 7 September 2014. Retrieved 7 September 2014.
Further reading
[edit]External links
[edit]- Jaipur Metro Rail Corporation Ltd.
- Jaipur Metro Guide Archived 4 March 2016 at the Wayback Machine