Windward Islands Bovenwindse Eilanden (Dutch) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Geography | |
| Location | Leeward Islands Lesser Antilles Caribbean Sea |
| Coordinates | 18°01′00″N 63°02′00″W / 18.0167°N 63.0333°W |
| Total islands | 3 |
| Major islands | Saba Saint Martin Sint Eustatius |
| Demographics | |
| Population | ~85.000 (2025 estimate) |
| Languages | |
The SSS islands (Dutch: SSS-eilanden), locally also known as the Dutch Windward Islands (Bovenwindse Eilanden or Bovenwinden), is a collective term for the three territories of the Dutch Caribbean (formerly the Netherlands Antilles) that are located within the Leeward Islands group of the Lesser Antilles in the Caribbean Sea.[1][2][3] In order of population size, they are: Sint Maarten, Sint Eustatius, and Saba. In some contexts, the term is also used to refer to the entire island of Saint Martin (which also includes the Collectivity of Saint Martin), alongside Sint Eustatius and Saba.
The SSS islands were island territories of the Netherlands Antilles, until its dissolution in 2010. Since then, Sint Maarten is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, while Sint Eustatius and Saba are special municipalities of the Netherlands. "SSS" is an acronym of the islands' names, and is analogous to the ABC, CAS, and BES islands, which are other commonly used subdivisions of the Dutch Caribbean.
History
[edit]The island of Saint Martin was split between France and the Netherlands in 1648.[4] The Dutch part, together with Sint Eustatius and Saba, became a single Dutch colony in 1815 as Sint Eustatius and Dependencies (Sint Eustatius en Onderhorigheden).[5] In 1828, this colony was merged with the colonies Curaçao and Dependencies (the ABC islands) and Surinam, with Paramaribo as its capital.[6] When this merger was partly reversed in 1845, the Dutch part of the SSS islands became part of Curaçao and Dependencies, with Willemstad as its capital.[7] This colony became the Netherlands Antilles in 1954.
As part of the Netherlands Antilles, the SSS islands initially formed a single island territory (eilandgebied) as the Windward Islands.[8] In 1983, it was split up into three separate island territories, each with a separate island council.[8] After the dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles on 10 October 2010, Sint Eustatius and Saba became special municipalities of the Netherlands, while Sint Maarten became an independent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands.[9]
Composition
[edit]Political composition
[edit]| Flag | Territory | Political status | Capital | Area | Population (Jan 2019) |
Population density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saba | Special municipality of the Netherlands | The Bottom | 13 km2 (5.0 sq mi) | 1,915 | 148/km2 (380/sq mi) | |
| Sint Eustatius | Special municipality of the Netherlands | Oranjestad | 21 km2 (8.1 sq mi) | 3,138 | 150/km2 (390/sq mi) | |
| Sint Maarten | Constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands | Philipsburg | 34 km2 (13 sq mi) | 41,486 | 1,221/km2 (3,160/sq mi) | |
| Total | 68 km2 (26 sq mi) | 46,539 | 684/km2 (1,770/sq mi) | |||
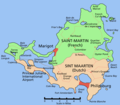
Geographical composition
[edit]| Map | Island | Country | Largest town | Area | Population (Jan 2019) |
Population density |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Saba | The Bottom | 13 km2 (5.0 sq mi) | 1,915 | 148/km2 (380/sq mi) | |
|
Saint Martin | Lower Prince's Quarter | 87 km2 (34 sq mi) | 73,666 | 847/km2 (2,190/sq mi) | |

|
Sint Eustatius | Oranjestad | 21 km2 (8.1 sq mi) | 3,138 | 150/km2 (390/sq mi) | |
| Total | 121 km2 (47 sq mi) | 78,719 | 651/km2 (1,690/sq mi) | |||
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Ghosh, Diptarka (16 May 2021). "Netherlands Antilles". WorldAtlas. Retrieved 18 April 2022.
The islands that are situated in the Leeward Islands are Saba, Sint Eustatius, and Sint Maarten. These islands are collectively referred to as the "SSS Islands"
- ^ "Netherlands Antilles (Windward Islands): Political Parties Material". Archives Hub. Jisc. Retrieved 18 April 2022.
With reference to the Netherlands Antilles, 'Windward Islands' (Bovenwindse Eilanden) means the north-eastern islands of Sint Maarten, Saba and Sint Eustatius, as opposed to the south-western islands of Aruba (which seceded from the Netherlands Antilles in 1986), Bonaire and Curaçao. Note that, confusingly, the Dutch 'Windward Islands' are considered to be part of the Leeward Island group, not the Windward Island group, in British English usage.
- ^ De Freitas, J. A.; Rojer, A. C.; Nijhof, B. S. J.; Houtepen, E. A. T.; Debrot, A. O. (2020). "Landscape Ecological Vegetation Map of St. Maarten (Lesser Antilles)". Archives Hub. Wageningen University & Research: 7.
Together with Saba and St. Eustatius, St. Maarten forms a cluster referred to as the Dutch Windward Islands (or "SSS" islands).
- ^ Van Aller 1994, p. 48
- ^ Van Aller 1994, p. 30
- ^ Van Aller 1994, p. 16
- ^ Van Aller 1994, p. 32
- ^ a b Van Aller 1994, p. 259
- ^ "Dutch Antilles dissolves as two new countries created". Reuters. 10 October 2010. Retrieved 18 April 2022.
Bibliography
[edit]- Van Aller, H. B. (1994). Van kolonie tot koninkrijksdeel: de staatkundige geschiedenis van de Nederlandse Antillen en Aruba van 1634 tot 1994 (PDF) (PhD thesis) (in Dutch). Groningen, Netherlands: Wolters-Noordhoff. doi:10.26481/dis.19940908ha. ISBN 9001045901. Retrieved 18 April 2022 – via Maastricht University.