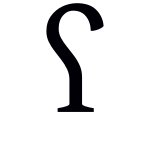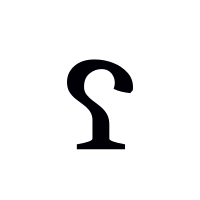| Voiced pharyngeal fricative | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ʕ | |||
| IPA number | 145 | ||
| Audio sample | |||
| Encoding | |||
| Entity (decimal) | ʕ | ||
| Unicode (hex) | U+0295 | ||
| X-SAMPA | ?\ | ||
| Braille | |||
| |||
| Voiced pharyngeal approximant | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ʕ̞ | |||
| |||
The voiced pharyngeal approximant or fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ⟨ʕ⟩. Epiglottals and epiglotto-pharyngeals are often mistakenly taken to be pharyngeal.
Although traditionally placed in the fricative row of the IPA chart, [ʕ] is usually an approximant. The IPA symbol itself is ambiguous, but no language is known to make a phonemic distinction between fricatives and approximants at this place of articulation.
The IPA letter ⟨ʕ⟩ is caseless. Capital ⟨⟩ and lower-case ⟨⟩ are pending at Unicode U+A7CE and U+A7CF.
Features
[edit]Features of the voiced pharyngeal approximant fricative:
- Its manner of articulation varies between approximant and fricative, which means it is produced by narrowing the vocal tract at the place of articulation, but generally not enough to produce much turbulence in the airstream. Languages do not distinguish voiced fricatives from approximants produced in the throat.
- Its place of articulation is pharyngeal, which means it is articulated with the tongue root against the back of the throat (the pharynx).
- Its phonation is voiced, which means the vocal cords vibrate during the articulation.
- It is an oral consonant, which means that air is exclusively allowed to escape through the mouth.
- It is a central consonant, which means it is produced by directing the airstream along the center of the tongue, rather than to the sides.
- Its airstream mechanism is pulmonic, which means it is articulated by pushing air solely with the intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles, as in most sounds.
Occurrence
[edit]Pharyngeal consonants are not widespread. Sometimes, a pharyngeal approximant develops from a uvular approximant. Many languages that have been described as having pharyngeal fricatives or approximants turn out on closer inspection to have epiglottal consonants instead. For example, the candidate /ʕ/ sound in Arabic and standard Hebrew (not modern Hebrew – Israelis generally pronounce this as a glottal stop) has been variously described as a voiced epiglottal fricative [ʢ], an epiglottal approximant [ʕ̞],[1] or a pharyngealized glottal stop [ʔˤ].[2]
| Language | Word | IPA | Meaning | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abaza | гӏапынхъамыз/g'apynkh"amyz | [ʕaːpənqaːməz] | 'March' | ||
| Afar | damaqtu | [dʌmʌʕtu] | 'male baboon' | ||
| Arabic | اَﻟْﻌَﺮَبِيَّةُ/al-ʽarabiyya | [alʕaraˈbijːa] | 'Arabic' | See Arabic phonology | |
| Assyrian | Eastern | ܬܪܥܐ/täroa | [tʌrʕɑ] | 'door' |
The majority of the speakers will pronounce the word as [tʌrɑ]. |
| Western | [tʌrʕɔ] | ||||
| Avar | гӀоркь/ⱨorꝗ/ﻋﻮٰرڨ | [ʕortɬʼː] | 'handle' | ||
| Chechen | Ӏан/jan/عـﺂن | ⓘ | 'winter' | ||
| Coeur d'Alene[3] | stʕin | [stʕin] | 'antelope' | ||
| Danish | Standard[4] | ravn | [ʕ̞ɑ̈wˀn] | 'raven' | An approximant;[4] also described as uvular [ʁ].[5] See Danish phonology |
| Dhao[6] | [ʕaa] | 'and' | Phonetic status is not clear, but it has "extremely limited distribution". It may not be pronounced at all or be realized as a glottal stop. | ||
| Dutch | Limburg[7] | rad | [ʕ̞ɑt] | 'wheel' | An approximant; a possible realization of /r/.[7] Realization of /r/ varies considerably among dialects. See Dutch phonology |
| German | Some speakers[8] | Mutter | [ˈmutɔʕ̞] | 'mother' | An approximant; occurs in East Central Germany, Southwestern Germany, parts of Switzerland and in Tyrol.[8] See Standard German phonology |
| Swabian dialect[9] | ändard | [ˈend̥aʕ̞d̥] | 'changes' | An approximant.[9] It's an allophone of /ʁ/ in nucleus and coda positions;[9] pronounced as a uvular approximant in onsets.[9] | |
| Hebrew | Iraqi | עִבְרִית/ʿivrît | [ʕibˈriːθ] | 'Hebrew language' | See Modern Hebrew phonology |
| Sephardi | [ʕivˈɾit] | ||||
| Yemenite | ⓘ | ||||
| Ingush | ӏаддал | [ʕaddal] | 'Archer' | ||
| Judaeo-Spanish [citation needed] | Haketia | ˁagzan | [ʕaɡˈzan] | 'lazy' | Borrowed from Arabic and Hebrew |
| Kabyle[10] | ɛemmi | [ʕəmːi] | 'my (paternal) uncle' | ||
| Kurdish | Kurmanji | ewr/'ewr | [ʕɜwr] | 'cloud' | The sound is usually not written in the Latin alphabet, but ⟨'⟩ can be used. |
| Khalaj | Standard | yâan | [jɑːɑ̯n] | 'side' | |
| Luwati | ﻗﻠـعـﺔ | [qilʕa] | 'castle' | Used in Arabic loanwords | |
| Malay | Kedah | باﮐﺮ/bakar | [ba.kaʕ] | 'burn' | Allophone of /r/ as word-final coda. Could be voiced velar fricative [ɣ] for some speakers.[11] |
| Maltese | għada | [ʕada] | 'tomorrow' | ||
| Mehri[12] | ﻋﻴن/ʾāyn | [ʕayn] | 'eye' | ||
| Nuu-chah-nulth | ʕiiniƛ | [ʕiːnitɬ] | 'dog' | May be a plosive /ʡ/ | |
| Occitan | Southern Auvergnat[citation needed] | pala | [ˈpaʕa] | 'shovel' | See Occitan phonology |
| Okanagan[13] | ʕaymt | [ʕajmt] | 'angry' | ||
| Sioux | Stoney | marazhud | [maʕaʒud] | 'rain' | |
| Somali | cunto/𐒋𐒚𐒒𐒂𐒙 | [ʕunto] | 'food' | See Somali phonology | |
| Soqotri[14] | أَﻋْﺮٞب/áˁreb | [aʕreb] | 'raven' | See Soqotri phonology | |
| Ukrainian | голос | [ˈʕɔlos] | 'voice' | Also described as glottal [ɦ]. See Ukrainian phonology | |
See also
[edit]- Modifier letter left half ring
- Index of phonetics articles
- Voiced uvular fricative
- Glottal stop
- Ayin
Citations
[edit]- ^ Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996:167–168)
- ^ Thelwall (1990)
- ^ Doak, Ivy Grace (1997). Coeur d'Alene grammatical relations (PhD dissertation). Austin: University of Texas.
- ^ a b Ladefoged & Maddieson (1996:323)
- ^ Basbøll (2005:62)
- ^ Grimes, Charles E. (1999). Dardjowidjojo, Soenjono; Nasanius, Yassir (eds.). Implikasi penelitian fonologis untuk cara menulis bahasa-bahasa daerah di Kawasan Timur Indonesia [Implications from phonological research for ways of writing vernacular languages in eastern Indonesia] (PDF). PELBBA 12: Pertemuan Linguistik (Pusat Kajian) Bahasa dan Budaya Atma Jaya Kedua Belas (in Indonesian). Yogyakarta: Kanisius. pp. 173–197.
- ^ a b Collins & Mees (2003:201)
- ^ a b Dudenredaktion, Kleiner & Knöbl (2015:51)
- ^ a b c d Hiller, Markus. "Pharyngeals and 'lax' vowel quality" (PDF). Mannheim: Institut für Deutsche Sprache. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2014-05-28. Retrieved 2015-02-24.
- ^ Bonafont (2006:9)
- ^ Mohamed, Noriah (June 2009). "The Malay Chetty Creole Language of Malacca: A Historical and Linguistic Perspective". Journal of the Malaysian Branch of the Royal Asiatic Society. 82 (1 (296)): 60. JSTOR 41493734.
- ^ Rubin, Aaron D. (2018). Omani Mehri: A New Grammar with Texts. Brill. p. 32. ISBN 978-90-04-36247-5.
- ^ Pattison, Lois Cornelia. "Douglas Lake Okanagan: Phonology and Morphology." University of British Columbia. 1978.
- ^ "SLOnline". soqotri-lexicon.ru. Retrieved 2025-07-02.
General references
[edit]- Basbøll, Hans (2005), The Phonology of Danish, Taylor & Francis, ISBN 0-203-97876-5
- Bonafont, Door Rosa (2006), Guia de conversa universitaria amazic-catala/Tamazight-Takatalant amalal usiwel asdawan, University of Barcelona, ISBN 9788447531141
- Collins, Beverley; Mees, Inger M. (2003) [First published 1981], The Phonetics of English and Dutch (5th ed.), Leiden: Brill Publishers, ISBN 9004103406
- Danylenko, Andrii; Vakulenko, Serhii (1995), Ukrainian, Lincom Europa, ISBN 9783929075083
- Dudenredaktion; Kleiner, Stefan; Knöbl, Ralf (2015) [First published 1962], Das Aussprachewörterbuch (in German) (7th ed.), Berlin: Dudenverlag, ISBN 978-3-411-04067-4
- Ladefoged, Peter; Maddieson, Ian (1996). The Sounds of the World's Languages. Oxford: Blackwell. ISBN 0-631-19815-6.
- Thelwall, Robin (1990). "Arabic". Journal of the International Phonetic Association. 20 (2): 37–41. doi:10.1017/S0025100300004266. S2CID 243640727.