Solar eclipse of April 17, 1912
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's ascending node of the orbit on April 17, 1912 (Gregorian Calendar) (April 4, 1912 in Julian Calendar, Russia, Turkey, and Balkans).[1][2] It was a hybrid event, starting and ending as an annular eclipse, with only a small portion of totality (only 1.3 km (0.808 mi or 4,265 feet) wide). A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.
Annularity was first visible from southeastern tip of Venezuela, northern tip of Brazil, British Guyana (today's Guyana), Dutch Guiana (today's Suriname) and Porto Santo Island in Madeira, Portugal, then totality from Portugal and Spain, with annularity continued northeast across France (including northwestern suburbs of Paris), Belgium, Netherlands, Germany and Russian Empire (the parts now belonging to northern Latvia, southern Estonia and Russia). Occurring 7.4 days after apogee (Apogee on April 10, 1912) and only 5.5 days before perigee (Perigee on April 22, 1912), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger.
It was the 30th eclipse of the 137th Saros cycle, which began with a partial eclipse on May 25, 1389, and will conclude with a partial eclipse on June 28, 2633. This eclipse occurred two days after the RMS Titanic sank in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean under the darkness of new moon.[3]
Observations
 The Observatory of Paris had the Globule balloon aloft for the 17 April 1912 hybrid eclipse, reported by Camille Flammarion.[4] |  The Le Petit Journal cover, on 1912 April 21, shows eclipse watchers in 1912 along with the solar eclipse of May 22, 1724, the previous total solar eclipse visible from Paris, France[5] |
 The 1 May 1912 edition of the luso-Brazilian Brasil-Portugal magazine publishes photographs of the eclipse, as it was seen in Lisbon. An editorial says: "One can tell, on that moment, the mathematical regularity that presides over everything that goes on above and the considerable achievements that the oldest of sciences — Astronomy — has been meeting. While some, strong spirits, point out the fact and point out how precise are scientific calculi, the others, believers, consider that what we can grasp is still too little and, not being able to conceive a Creation without a Creator, pay homage to science but continue to kneel before God. The reader can judge the interest that the phenomenon sparked among us by himself though the photographs that follow, where one can see it all; the wise and the godless, the noble and the commoners, women and men, everyone paid no attention to earthly matters and, for a moment, observed with better or worse instruments what was going on up above. It was even a momentaneous rest for politics." |
|
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses 1910–1913
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[6]
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1910 to 1913 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||
| 117 | May 9, 1910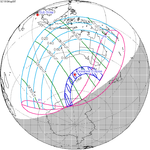 Total | 122 | November 2, 1910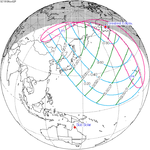 Partial | |
| 127 | April 28, 1911 Total | 132 | October 22, 1911 Annular | |
| 137 | April 17, 1912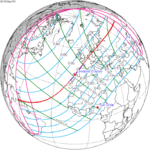 Hybrid | 142 | October 10, 1912 Total | |
| 147 | April 6, 1913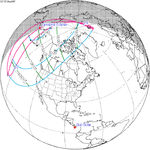 Partial | 152 | September 30, 1913 Partial | |
Saros 137
It is a part of Saros cycle 137, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, containing 70 events. The series started with partial solar eclipse on May 25, 1389. It contains total eclipses from August 20, 1533, through December 6, 1695, first set of hybrid eclipses from December 17, 1713, through February 11, 1804, first set of annular eclipses from February 21, 1822, through March 25, 1876, second set of hybrid eclipses from April 6, 1894, through April 28, 1930, and second set of annular eclipses from May 9, 1948, through April 13, 2507. The series ends at member 70 as a partial eclipse on June 28, 2633. The longest duration of totality was 2 minutes, 55 seconds on September 10, 1569. Solar Saros 137 has 55 umbral eclipses from August 20, 1533, through April 13, 2507 (973.62 years). That is almost 1 millennium.
| Series members 30–40 occur between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 31 | 32 |
 April 17, 1912 |  April 28, 1930 |  May 9, 1948 |
| 33 | 34 | 35 |
 May 20, 1966 |  May 30, 1984 |  June 10, 2002 |
| 36 | 37 | 38 |
 June 21, 2020 |  July 2, 2038 |  July 12, 2056 |
| 39 | 40 | |
 July 24, 2074 |  August 3, 2092 | |
Notes
- ^ "TO'DAY'S ECLIPSE OF THE SUN". The Guardian. London, Greater London, England. 1912-04-17. p. 16. Retrieved 2023-11-04 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Few saw eclipse". The Brooklyn Daily Eagle. Brooklyn, New York. 1912-04-17. p. 20. Retrieved 2023-11-04 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ www.astronomeer.com: The "Titanic" eclipse of 17 April 1912 Archived 7 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine The last annular eclipse in the Netherlands was 17 April 1912, just two days after the Titanic hit an iceberg and sank.
- ^ [1] Archived 2009-05-30 at the Wayback Machine Societe Astronomique, pp. 234–248, 1912 – By Camille Flammarion (Translation from French by LRM) p. 240 "A balloon dirigible, having on board Admiral Fournier and Colonel Bourgeois permitted good perception of the moon's shadow at a speed of 800 m/sec ... From a captive balloon near Saint-Nom-de-la-Breteche, Captain Dupic made analogous observations which confirmed those made from the dirigible."
- ^ [2] 17th April 1912: Eclipse fever grips Europe Archived 2011-07-16 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
References
- Earth visibility chart and eclipse statistics Eclipse Predictions by Fred Espenak, NASA/GSFC
- Google interactive map
- Besselian elements
- Photo of Solar Corona April 17, 1912
- Russia expedition for solar eclipse of April 17, 1912 Archived August 9, 2009, at the Wayback Machine
- The Eclipse of April 17, 1912 as Visible in France Popular Astronomy, vol. 20, pp. 372–375, [3]
- [4] Flickr photo of eclipse watchers from France
- v
- t
- e
| By era | |
|---|---|
| Saros series (list) | |
| Visibility | |
| Historical |
|

Total/hybrid eclipses
→ next total/hybrid
- 1133
- 1185
- 1560
- 1598
- 1652
- 1654
- 1673
- 1706
- 1715
- 1724
- 1766
- 1778
- 1780
- 1806
- 1816
- 1824
- 1842
- 1851
- 1853
- 1857
- 1858
- 1860
- 1865
- 1867
- 1868
- 1869
- 1870
- 1871
- 1874
- 1875
- 1878
- 1882
- 1883
- 1885
- 1886
- 1887
- Jan. 1889
- Dec. 1889
- 1893
- 1896
- 1898
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- Jan. 1908
- Dec. 1908
- 1909
- 1910
- 1911
- Apr. 1912
- Oct. 1912
- 1914
- 1916
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1928
- 1929
- Apr. 1930
- Oct. 1930
- 1932
- 1934
- 1936
- 1937
- 1938
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jan. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- 1952
- 1954
- 1955
- 1956
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- 1967
- 1968
- 1970
- 1972
- 1973
- 1974
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1985
- 1986
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1997
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- 2024
- → 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2033
- 2034
- 2035
- 2037
- 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2050
- 2052
- 2053
- 2055
- Jan. 2057
- Dec. 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2068
- 2070
- 2071
- 2072
- 2073
- 2075
- 2076
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- 2086
- 2088
- 2089
- 2090
- 2091
- 2093
- 2094
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100
- 2186

Annular eclipses
→ next annular
- 1820
- 1854
- 1879
- 1889
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- 1908
- 1911
- 1914
- Feb. 1915
- Aug. 1915
- 1916
- 1917
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1929
- 1932
- Feb. 1933
- Aug. 1933
- 1934
- 1935
- 1936
- 1937
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jul. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- Mar. 1951
- Sep. 1951
- 1952
- Jan. 1954
- Dec. 1954
- 1955
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- Mar. 1969
- Sep. 1969
- 1970
- 1972
- Jan. 1973
- Dec. 1973
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2014
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- → 2024
- 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2032
- 2034
- 2035
- 2036
- Jan. 2038
- Jul. 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2052
- 2053
- Jan. 2056
- Jul. 2056
- 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2070
- 2071
- Jan. 2074
- Jul. 2074
- 2075
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- Jun. 2085
- Dec. 2085
- 2088
- 2089
- Feb. 2092
- Aug. 2092
- 2093
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100

Partial eclipses
→ next partial
- Jan. 1639
- Apr. 1902
- May 1902
- Oct. 1902
- Feb. 1906
- Jul. 1906
- Aug. 1906
- Dec. 1909
- Nov. 1910
- Apr. 1913
- Aug. 1913
- Sep. 1913
- Dec. 1916
- Jan. 1917
- Jun. 1917
- Jul. 1917
- May 1920
- Nov. 1920
- Mar. 1924
- Jul. 1924
- Aug. 1924
- Dec. 1927
- Jun. 1928
- Nov. 1928
- Apr. 1931
- Sep. 1931
- Oct. 1931
- Jan. 1935
- Feb. 1935
- Jun. 1935
- Jul. 1935
- Nov. 1938
- Mar. 1942
- Aug. 1942
- Sep. 1942
- Jan. 1946
- May 1946
- Jun. 1946
- Nov. 1946
- Apr. 1949
- Oct. 1949
- Feb. 1953
- Jul. 1953
- Aug. 1953
- Dec. 1956
- Mar. 1960
- Sep. 1960
- Jan. 1964
- Jun. 1964
- Jul. 1964
- Dec. 1964
- May 1967
- Mar. 1968
- Feb. 1971
- Jul. 1971
- Aug. 1971
- Dec. 1974
- May 1975
- Nov. 1975
- Apr. 1978
- Oct. 1978
- Jan. 1982
- Jun. 1982
- Jul. 1982
- Dec. 1982
- May 1985
- Apr. 1986
- Mar. 1989
- Aug. 1989
- Dec. 1992
- May 1993
- Nov. 1993
- Apr. 1996
- Oct. 1996
- Sep. 1997
- Feb. 2000
- 1 Jul. 2000
- 31 Jul. 2000
- Dec. 2000
- Apr. 2004
- Oct. 2004
- Mar. 2007
- Sep. 2007
- Jan. 2011
- Jun. 2011
- Jul. 2011
- Nov. 2011
- Oct. 2014
- Sep. 2015
- Feb. 2018
- Jul. 2018
- Aug. 2018
- Jan. 2019
- Apr. 2022
- Oct. 2022
- → Mar. 2025
- Sep. 2025
- Jan. 2029
- Jun. 2029
- Jul. 2029
- Dec. 2029
- 2032
- 2033
- Feb. 2036
- Jul. 2036
- Aug. 2036
- 2037
- May 2040
- Nov. 2040
- Jan. 2047
- Jun. 2047
- Jul. 2047
- Dec. 2047
- 2050
- Apr. 2051
- Oct. 2051
- Mar. 2054
- Aug. 2054
- Sep. 2054
- 2055
- May 2058
- Jun. 2058
- Nov. 2058
- Mar. 2062
- Sep. 2062
- Feb. 2065
- Jul. 2065
- Aug. 2065
- Dec. 2065
- 2068
- Apr. 2069
- May 2069
- Oct. 2069
- 2072
- 2073
- Jun. 2076
- Jul. 2076
- Nov. 2076
- Feb. 2083
- Jul. 2083
- Aug. 2083
- 2084
- 2086
- May 2087
- Jun. 2087
- Oct. 2087
- 2090
- 2091
- Jun. 2094
- Jul. 2094
- Dec. 2094
- Apr. 2098
- Sep. 2098
- Oct. 2098
 Astronomy portal
Astronomy portal Solar System portal
Solar System portal Category
Category
















