Solar eclipse of January 6, 2019

The solar eclipse of January 6, 2019 was a partial solar eclipse that was visible in East Asia and the North Pacific.[1]
Visibility
The maximal phase (71%) of the partial eclipse was recorded in Sakha Republic (Russia).
The eclipse was observed in Japan, the Russian Far East, North and South Korea, eastern China, eastern Mongolia and northwest Alaska.
Gallery
-
 Jinan, China, 00:18 UTC
Jinan, China, 00:18 UTC -
 Bohyeonsan, South Korea, 00:47 UTC
Bohyeonsan, South Korea, 00:47 UTC -
 Aichi Prefecture, Japan, 01:00 UTC
Aichi Prefecture, Japan, 01:00 UTC
Related eclipses
Eclipses of 2019
- A partial solar eclipse on January 6.
- A total lunar eclipse on January 21.
- A total solar eclipse on July 2.
- A partial lunar eclipse on July 16.
- An annular solar eclipse on December 26.
Tzolkinex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of November 25, 2011
- Followed: Solar eclipse of February 17, 2026
Half-Saros cycle
- Preceded: Lunar eclipse of December 31, 2009
- Followed: Lunar eclipse of January 12, 2028
Tritos
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of February 7, 2008
- Followed: Solar eclipse of December 5, 2029
Solar Saros 122
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of December 25, 2000
- Followed: Solar eclipse of January 16, 2037
Inex
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of January 26, 1990
- Followed: Solar eclipse of December 16, 2047
Triad
- Preceded: Solar eclipse of March 7, 1932
- Followed: Solar eclipse of November 6, 2105
Solar eclipses of 2018–2021
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[2]
Note: Partial solar eclipses on February 15, 2018, and August 11, 2018, occurred during the previous semester series.
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
117 Partial from Melbourne, Australia | 2018 July 13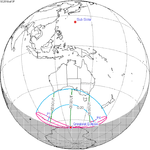 Partial | −1.35423 | 122 Partial from Nakhodka, Russia | 2019 January 6 Partial | 1.14174 | |
127 La Serena, Chile | 2019 July 2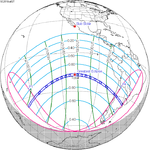 Total | −0.64656 | 132 Jaffna, Sri Lanka | 2019 December 26 Annular | 0.41351 | |
137 Beigang, Yunlin, Taiwan | 2020 June 21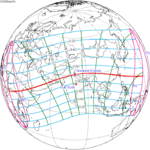 Annular | 0.12090 | 142 Gorbea, Chile | 2020 December 14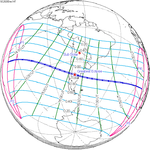 Total | −0.29394 | |
147 Partial from Halifax, Canada | 2021 June 10 Annular | 0.91516 | 152 From HMS Protector off South Georgia | 2021 December 4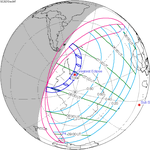 Total | −0.95261 | |
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days). All eclipses in this table occur at the Moon's descending node.
| 21 eclipse events between June 1, 2011 and June 1, 2087 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| May 31 – June 1 | March 19–20 | January 5–6 | October 24–25 | August 12–13 |
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 June 1, 2011 | 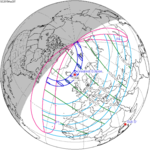 March 20, 2015 |  January 6, 2019 | 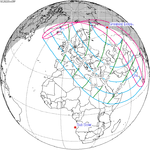 October 25, 2022 | 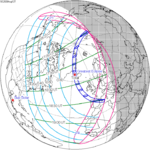 August 12, 2026 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 June 1, 2030 | 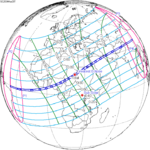 March 20, 2034 | 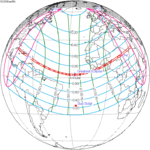 January 5, 2038 |  October 25, 2041 | 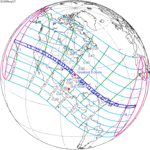 August 12, 2045 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 May 31, 2049 |  March 20, 2053 |  January 5, 2057 |  October 24, 2060 |  August 12, 2064 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | 156 |
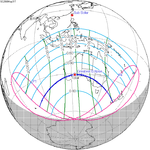 May 31, 2068 |  March 19, 2072 |  January 6, 2076 | 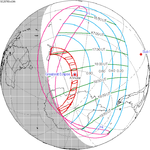 October 24, 2079 | 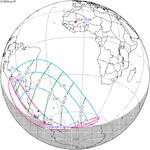 August 13, 2083 |
| 158 | 160 | 162 | 164 | 166 |
 June 1, 2087 |  October 24, 2098 | |||
References

External links
- http://eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov/SEplot/SEplot2001/SE2019Jan06P.GIF
- v
- t
- e
| By era | |
|---|---|
| Saros series (list) | |
| Visibility | |
| Historical |
|

Total/hybrid eclipses
→ next total/hybrid
- 1133
- 1185
- 1560
- 1598
- 1652
- 1654
- 1673
- 1706
- 1715
- 1724
- 1766
- 1778
- 1780
- 1806
- 1816
- 1824
- 1842
- 1851
- 1853
- 1857
- 1858
- 1860
- 1865
- 1867
- 1868
- 1869
- 1870
- 1871
- 1874
- 1875
- 1878
- 1882
- 1883
- 1885
- 1886
- 1887
- Jan. 1889
- Dec. 1889
- 1893
- 1896
- 1898
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- Jan. 1908
- Dec. 1908
- 1909
- 1910
- 1911
- Apr. 1912
- Oct. 1912
- 1914
- 1916
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1928
- 1929
- Apr. 1930
- Oct. 1930
- 1932
- 1934
- 1936
- 1937
- 1938
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jan. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- 1952
- 1954
- 1955
- 1956
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- 1967
- 1968
- 1970
- 1972
- 1973
- 1974
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1985
- 1986
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1997
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- 2024
- → 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2033
- 2034
- 2035
- 2037
- 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2050
- 2052
- 2053
- 2055
- Jan. 2057
- Dec. 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2068
- 2070
- 2071
- 2072
- 2073
- 2075
- 2076
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- 2086
- 2088
- 2089
- 2090
- 2091
- 2093
- 2094
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100
- 2186

Annular eclipses
→ next annular
- 1820
- 1854
- 1879
- 1889
- 1900
- 1901
- 1903
- 1904
- 1905
- 1907
- 1908
- 1911
- 1914
- Feb. 1915
- Aug. 1915
- 1916
- 1917
- 1918
- 1919
- 1921
- 1922
- 1923
- 1925
- 1926
- 1927
- 1929
- 1932
- Feb. 1933
- Aug. 1933
- 1934
- 1935
- 1936
- 1937
- 1939
- 1940
- 1941
- 1943
- Jul. 1944
- 1945
- 1947
- 1948
- 1950
- Mar. 1951
- Sep. 1951
- 1952
- Jan. 1954
- Dec. 1954
- 1955
- 1957
- 1958
- 1959
- 1961
- 1962
- 1963
- 1965
- 1966
- Mar. 1969
- Sep. 1969
- 1970
- 1972
- Jan. 1973
- Dec. 1973
- 1976
- 1977
- 1979
- 1980
- 1981
- 1983
- 1984
- 1987
- 1988
- 1990
- 1991
- 1992
- 1994
- 1995
- 1998
- 1999
- 2001
- 2002
- 2003
- 2005
- 2006
- 2008
- 2009
- 2010
- 2012
- 2013
- 2014
- 2016
- 2017
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2023
- → 2024
- 2026
- 2027
- 2028
- 2030
- 2031
- 2032
- 2034
- 2035
- 2036
- Jan. 2038
- Jul. 2038
- 2039
- 2041
- 2042
- 2043
- 2044
- 2045
- 2046
- 2048
- 2049
- 2052
- 2053
- Jan. 2056
- Jul. 2056
- 2057
- 2059
- 2060
- 2061
- 2063
- 2064
- 2066
- 2067
- 2070
- 2071
- Jan. 2074
- Jul. 2074
- 2075
- 2077
- 2078
- 2079
- 2081
- 2082
- 2084
- Jun. 2085
- Dec. 2085
- 2088
- 2089
- Feb. 2092
- Aug. 2092
- 2093
- 2095
- 2096
- 2097
- 2099
- 2100

Partial eclipses
→ next partial
- Jan. 1639
- Apr. 1902
- May 1902
- Oct. 1902
- Feb. 1906
- Jul. 1906
- Aug. 1906
- Dec. 1909
- Nov. 1910
- Apr. 1913
- Aug. 1913
- Sep. 1913
- Dec. 1916
- Jan. 1917
- Jun. 1917
- Jul. 1917
- May 1920
- Nov. 1920
- Mar. 1924
- Jul. 1924
- Aug. 1924
- Dec. 1927
- Jun. 1928
- Nov. 1928
- Apr. 1931
- Sep. 1931
- Oct. 1931
- Jan. 1935
- Feb. 1935
- Jun. 1935
- Jul. 1935
- Nov. 1938
- Mar. 1942
- Aug. 1942
- Sep. 1942
- Jan. 1946
- May 1946
- Jun. 1946
- Nov. 1946
- Apr. 1949
- Oct. 1949
- Feb. 1953
- Jul. 1953
- Aug. 1953
- Dec. 1956
- Mar. 1960
- Sep. 1960
- Jan. 1964
- Jun. 1964
- Jul. 1964
- Dec. 1964
- May 1967
- Mar. 1968
- Feb. 1971
- Jul. 1971
- Aug. 1971
- Dec. 1974
- May 1975
- Nov. 1975
- Apr. 1978
- Oct. 1978
- Jan. 1982
- Jun. 1982
- Jul. 1982
- Dec. 1982
- May 1985
- Apr. 1986
- Mar. 1989
- Aug. 1989
- Dec. 1992
- May 1993
- Nov. 1993
- Apr. 1996
- Oct. 1996
- Sep. 1997
- Feb. 2000
- 1 Jul. 2000
- 31 Jul. 2000
- Dec. 2000
- Apr. 2004
- Oct. 2004
- Mar. 2007
- Sep. 2007
- Jan. 2011
- Jun. 2011
- Jul. 2011
- Nov. 2011
- Oct. 2014
- Sep. 2015
- Feb. 2018
- Jul. 2018
- Aug. 2018
- Jan. 2019
- Apr. 2022
- Oct. 2022
- → Mar. 2025
- Sep. 2025
- Jan. 2029
- Jun. 2029
- Jul. 2029
- Dec. 2029
- 2032
- 2033
- Feb. 2036
- Jul. 2036
- Aug. 2036
- 2037
- May 2040
- Nov. 2040
- Jan. 2047
- Jun. 2047
- Jul. 2047
- Dec. 2047
- 2050
- Apr. 2051
- Oct. 2051
- Mar. 2054
- Aug. 2054
- Sep. 2054
- 2055
- May 2058
- Jun. 2058
- Nov. 2058
- Mar. 2062
- Sep. 2062
- Feb. 2065
- Jul. 2065
- Aug. 2065
- Dec. 2065
- 2068
- Apr. 2069
- May 2069
- Oct. 2069
- 2072
- 2073
- Jun. 2076
- Jul. 2076
- Nov. 2076
- Feb. 2083
- Jul. 2083
- Aug. 2083
- 2084
- 2086
- May 2087
- Jun. 2087
- Oct. 2087
- 2090
- 2091
- Jun. 2094
- Jul. 2094
- Dec. 2094
- Apr. 2098
- Sep. 2098
- Oct. 2098
 Astronomy portal
Astronomy portal Solar System portal
Solar System portal Category
Category
 | This solar eclipse–related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
- v
- t
- e

















